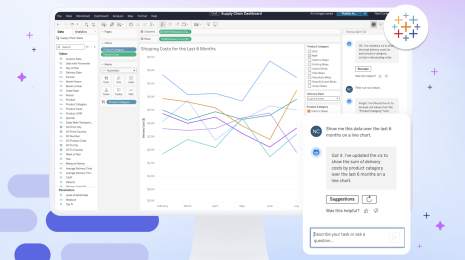
Ensuring AI Accuracy in Agentic Analytics
AI is proving to be great at many things. But when you break down its most primitive attributes, it’s good at one core thing: making challenging tasks easier for more people. When we deploy AI to help with data analytics and business intelligence, this continues to hold true.
At Tableau, our mission is to help people see, understand, and act on data. Even more, we want this mission to resonate with everyone by making actionable insights accessible to all. To do this effectively, those insights need to be trusted. Achieving that trust is simple in principle: insights must be consistently accurate, and relevant to the question. In practice, this is a hard problem to solve. It means avoiding hallucinations, which becomes more challenging when the questions are either too ambiguous or too complex.
So how do we achieve agentic data Q&A with trusted, relevant, and personalized results? Well I’m glad you asked.
A framework for agentic AI system validation
Like with all software, we need to internally validate a system’s quality before we feel comfortable letting anyone else use it. This philosophy rings true with AI quality as well; however, the approach to evaluating non-deterministic results can be quite a bit different.
Understanding accuracy
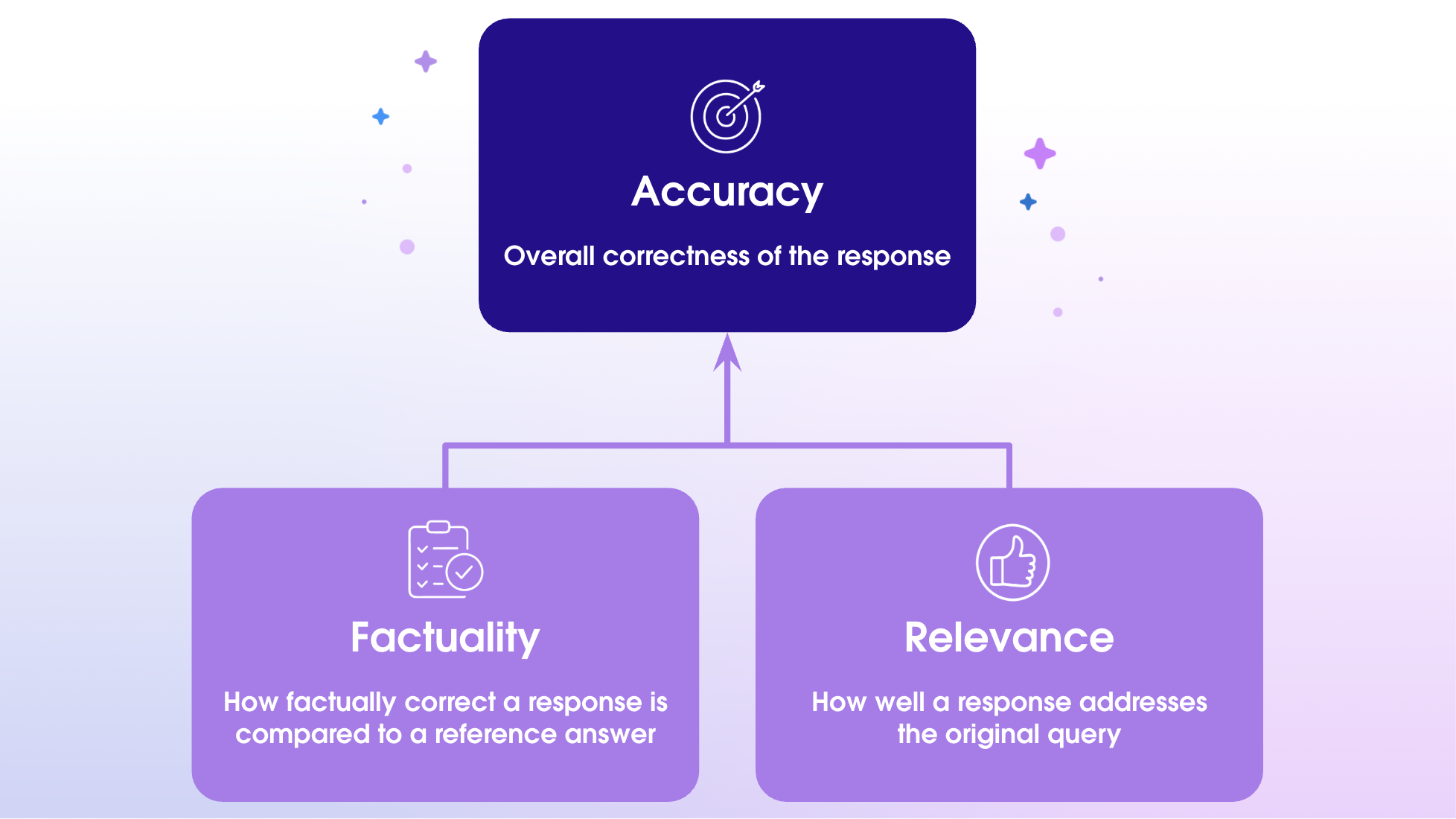
First, we need to have a shared understanding of what accuracy means to us. Internally, we use:
Accuracy = (0.5 x Factuality) + (0.5 x Relevance)
Where:
- Factuality: Is the system retrieving factually correct data?
- Relevance: Does the system present relevant insights that directly answer the question?
- 50% factuality + 50% relevance: A design decision that emphasizes that both aspects are equally important in analytical domains.
Judging AI accuracy for reliable results
To assess factuality and relevance, we need a subjective evaluation method. The subjectiveness is a result of the nondeterministic output. Or, more specifically, that two results can be different and accurate at the same time. And there are no tools based on heuristics that will reliably evaluate this. So to achieve this, we have deployed several methods:
- Human judging: Our team, quantifying the correctness, often considering factuality, coherence, relevance, and explainability. This is the utmost trusted method, but over time becomes expensive and time-consuming.
- AI judging: We can lean on reasoning models that behave more like human judging. While capable, they’re also proving to be as accurate as humans in many cases. And as such, can help with scale—yet at the burden of needing continued calibration with human judgements.
- Program judging: Correct retrieval of relevant data is a prerequisite to an accurate, factually correct, and relevant answer. The correctness of source data can be validated precisely through programmatic comparison.
Verification approaches and iterative AI enhancements
Step 1: Benchmark
Improving the quality of our agentic components starts with setting up a good way to test and improve them. To do this, we deploy a modern evaluation framework, which includes the following components:
Golden dataset test suites
Our datasets represent a substantial investment in our infrastructure. These are test cases that simulate authentic user interactions and include detailed annotations. These annotations serve as ground truth, featuring labels that facilitate the categorization of evaluation results. This structured approach enhances our understanding of performance and directs our optimization efforts.
Calibrated metrics
As AI systems become more sophisticated, validating their absolute correctness becomes increasingly difficult. The selection and application of quality metrics are paramount. The process of identifying and refining metrics that are dependable and reliable can take substantial time and effort. Once their effectiveness is substantiated, these are referred to as calibrated metrics.
Evaluation loops
- E2E evaluation (outer loop): The evaluation runner then executes tests and provides scores. Our runner facilitates end-to-end evaluation through integration with an internal deployment of our agentic capabilities.
- Component evaluation (inner loop): Optimizing for the full end-to-end process proves to be slow and inefficient. Therefore, we integrate components into the evaluation framework incrementally, allowing us to focus on refining each part independently. This necessitates adapting our golden datasets to serve as test inputs for these individual components.
Step 2: Breadth
The accuracy of AI in agentic analytics is assessed with the development of our evaluation framework. Initially, a foundational set of "golden examples" will be established to serve as a baseline for testing and iterative refinement.
In pursuit of continuous improvement, this dataset is augmented weekly. We focus our effort on the diversity of tasks and the diversity of domains when expanding the dataset. If any gap in the dataset is detected—through customer feedback or other means—we actively craft new examples to bridge the gap in an ASAP manner. This incremental expansion facilitates the scalable growth of our evaluation efforts, ensuring the framework's capacity to accommodate an increasingly diverse range of data.
We acknowledge that mislabeled data within the golden examples, or inadequately calibrated metrics, can be issues we run into. To defend against this, we dedicate efforts to identifying and remediating any issues, recognizing them as critical steps in constructing a robust and reliable evaluation system.
Notwithstanding these framework and dataset challenges, we discover genuine quality issues within AI components. These actual performance problems will prove invaluable in directing improvement efforts and refining our AI models. Our iterative process of measurement, evaluation, and refinement is designed to address both the fundamental integrity of our evaluation system and the overall quality of our AI responses.
Step 3: Interpret
Interpretation is to make sense of evaluation results by spotting trends and deciding what to fix first. We do this by first making a list of all the issues we find, counting how many times each type of problem shows up, and keeping track of which specific examples in our good data are affected. This detailed breakdown helps us figure out what's most important to tackle, so we can put our energy where it'll make the biggest difference.
A significant part of our plan is to invest in a purpose-built, Integrated Development Environment (IDE), aimed to be like a regular coding IDE, but tailored for what an AI engineer needs. The goal is to boost productivity by smoothing out complex tasks and reducing the mental heavy lifting that comes with manual analysis.
Beyond just making the user interface and features better, our plan to streamline things also includes smart use of artificial intelligence itself. We picture using AI to automatically go through and sort our evaluation results. This smart automation will really speed up finding patterns and categorizing issues, cutting down on manual work even more. This lets our AI engineers focus on bigger-picture problem-solving and strategic improvements instead of sorting through data again and again.
Step 4: Optimize
We adopt a strategic approach to improvement, focusing on iterative enhancements. This involves prioritizing specific areas, optimizing them, and then proceeding to the next. The emphasis is on rapid iteration and observable results.
The process entails identifying critical issues through data-driven analysis. Upon pinpointing an area, our ML/AI engineers will compile a feature test suite on the problem area, and then employ various techniques, including data sanitization, model fine-tuning, and adjustments to user interaction mechanisms. Following each modification, a validation step on the feature suite will be conducted to assess its impact, as well as on previous tests to assess potential regression. This iterative cycle of refinement will continue until the desired outcome is achieved.
Our engineers will be equipped with a robust set of tools and methodologies to address diverse challenges. This capability will enable continuous improvement in the accuracy and reliability of our analytics, ultimately yielding more profound insights.
Customer validation to ensure agentic AI accuracy
We are also deeply investing in methods and new capabilities for our customers to further evaluate the efficacy of the analytical agents they deploy, particularly as it pertains to their larger data and metadata system.
While our current methods build confidence in quality and trust, we recognize that the metadata influencing agents via prompts will also dramatically affect quality. To ensure users receive accurate and reliable answers from these agents, subject matter experts need provisions for self-service agent testing and calibration tools.
This will empower these experts to fine-tune the agents to align with their organization's specific analytics needs, driven by their data, semantic models, terminology, and other custom definitions—ultimately creating a more accurate and personalized Q&A experience for their users.
You will learn more about these capabilities as they are released over the course of this year and early 2026. In the meantime, see how conversational analytics works with Tableau Next and learn more about how its AI-powered semantics enable trustworthy agentic analytics.